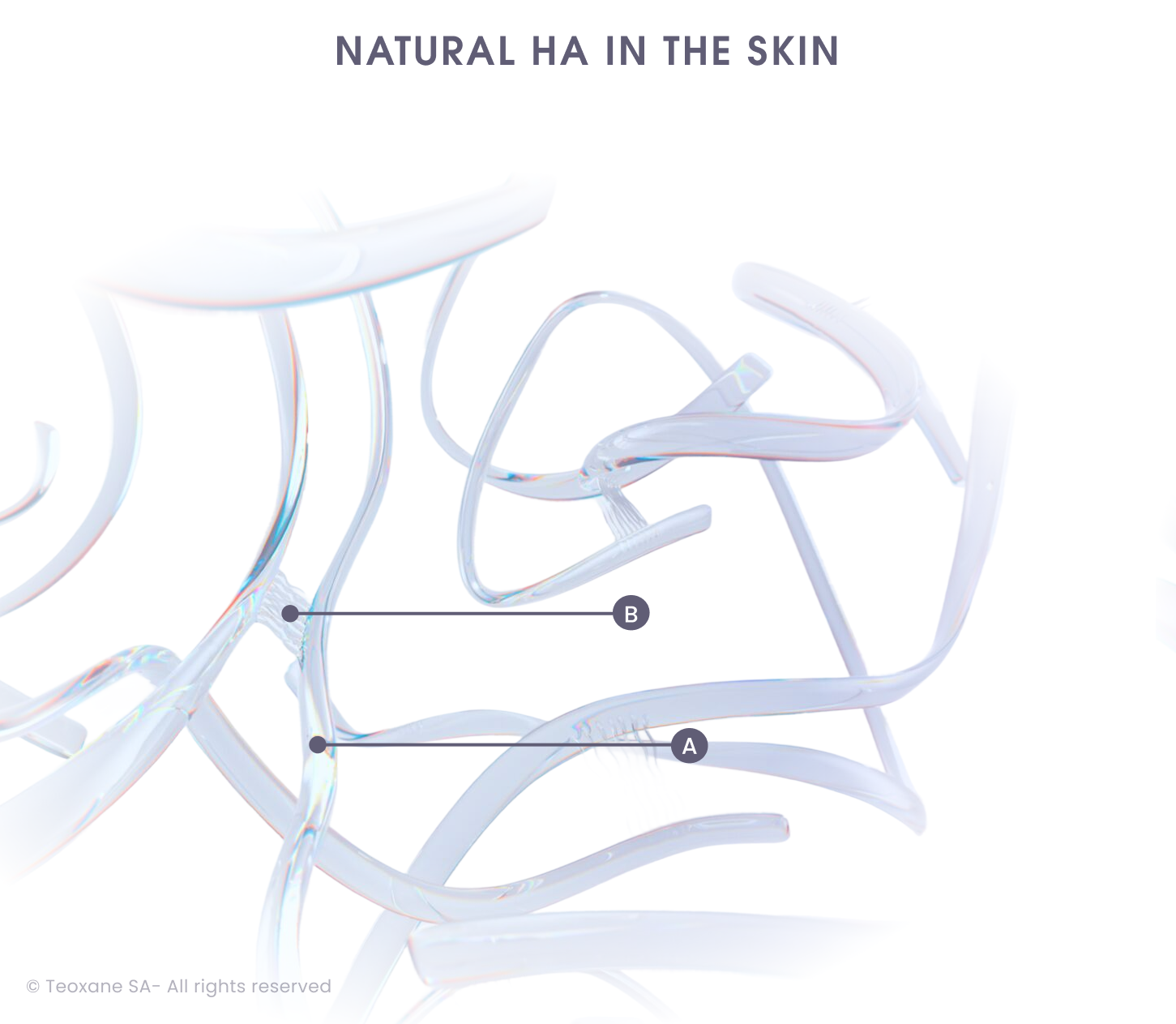
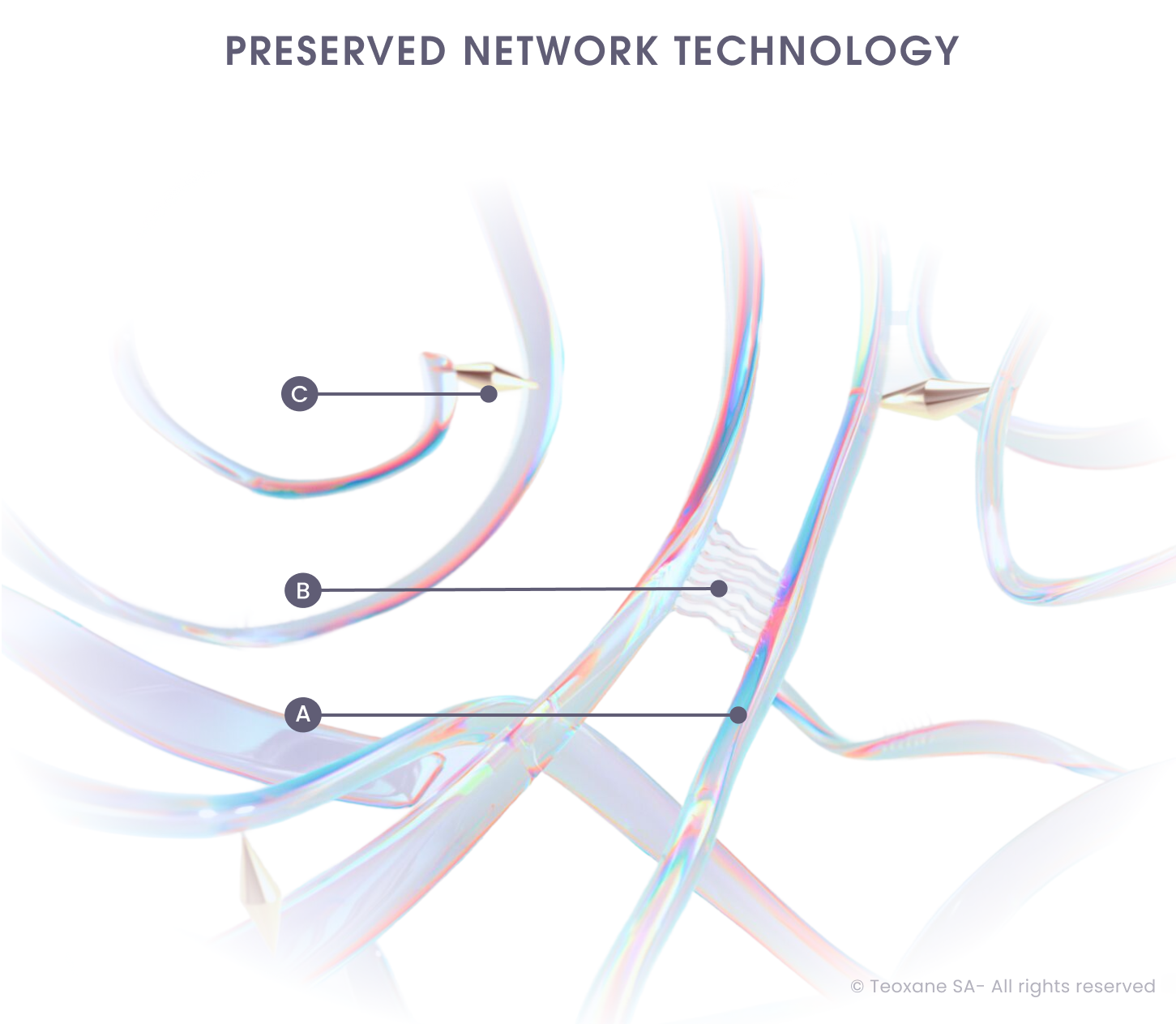
The Teoxane RHA® Collection includes hyaluronic acid (HA)
fillers with lidocaine and mepivacaine. Revance will only distribute the
Teoxane RHA® Collection with mepivacaine, thus may refer to the products without the use
of "Mepi" in the product name. The long-term efficacy and safety outcomes of
RHA® with lidocaine are applicable to RHA® with mepivacaine,
and mepivacaine has shown no significant impact on gel properties, including
rheology and degradation profile.
PLEASE SEE FULL DIRECTIONS FOR USE
RHA® Collection of Fillers, by Teoxane
Indications The Teoxane RHA® Collection of resilient hyaluronic acid (HA)
fillers includes RHA Redensity®, RHA® 2, RHA® 3 and RHA® 4 with lidocaine and RHA Redensity® Mepi,
RHA® 2 Mepi, RHA® 3 Mepi and RHA® Dynamic Volume,
with mepivacaine.
RHA Redensity® and RHA Redensity® Mepi are indicated
for injection into the dermis and superficial dermis of the face, for the
correction of moderate to severe dynamic perioral rhytids in adults 22 or
older. RHA® 2 and RHA® 2 Mepi are indicated for
injection into the mid-to-deep dermis for the correction of moderate to
severe dynamic facial wrinkles and folds, such as nasolabial folds (NLFs)
in adults 22 or older. RHA® 3 and RHA® 3 Mepi are
indicated for injection into the mid-to-deep dermis for the correction of
moderate to severe dynamic facial wrinkles and folds, such as nasolabial
folds (NLFs) and is also indicated for injection into the vermillion body,
vermillion border and oral commissure to achieve lip augmentation and lip
fullness in adults 22 or older. RHA® 4 is indicated for
injection in the deep dermis to superficial subcutaneous tissue for the
correction of moderate to severe dynamic facial wrinkles and folds, such
as nasolabial folds (NLFs) in adults 22 or older. RHA® Dynamic Volume
is indicated for injection in the deep dermis to superficial subcutaneous tissue
for the correction of moderate to severe dynamic facial wrinkles and folds,
such as nasolabial folds (NLFs) and for injection into the subcutaneous to supraperiosteal
layers for cheek augmentation and/or correction of age-related midface contour
deficiencies in adults 22 or older.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindications
Do not use in patients who have severe allergies, marked by a history of
anaphylaxis or multiple severe allergies, or in patients with a history of
allergies to gram-positive bacterial proteins or local anesthetics of the
amide type, such as lidocaine and mepivacaine.
Do not use in patients with bleeding disorders.
Warnings
Do not inject into blood vessels. Introduction of these products into the
vasculature may lead to embolization, occlusion of the vessels, ischemia,
or infarction. Take extra care when injecting soft-tissue fillers; for
example, inject the product slowly and apply the least amount of pressure
necessary. Rare, but serious, adverse events associated with the
intravascular injection of soft-tissue fillers in the face have been
reported and include temporary or permanent vision impairment, blindness,
cerebral ischemia or cerebral hemorrhage leading to stroke, skin necrosis,
and damage to underlying facial structures.
Immediately stop the injection if a patient exhibits any of the following
symptoms: changes in vision, signs of a stroke, blanching of the skin, or
unusual pain during or shortly after the procedure. Patients should
receive prompt medical attention and, possibly, evaluation by an
appropriate healthcare professional specialist should an intravascular
injection occur.
Product use at specific sites in which an active inflammatory process or
infection is present should be deferred until the underlying process has
been controlled.
Precautions
These products should only be used by healthcare professionals who have
appropriate training, experience, and knowledge of facial anatomy.
Discuss the potential risks of soft-tissue injections with your patients
prior to treatment and ensure that patients are aware of signs and
symptoms of potential complications.
The safety and effectiveness for the treatment of anatomic regions other
than the labeled indications have not been established in controlled U.S.
clinical studies
As with all transcutaneous procedures, dermal filler implantation carries a
risk of infection. Standard precautions associated with injectable materials
should be followed.
The safety for use in sites in the presence of other implants, during
pregnancy, in breastfeeding females, and in patients with known
susceptibility to keloid formation, hypertrophic scarring, and
pigmentation disorders has not been studied.
Use with caution in patients on immunosuppressive therapy.
Patients who are using products that can prolong bleeding (such as
thrombolytics, anticoagulants, or inhibitors of platelet aggregation) may
experience increased bruising or bleeding at treatment sites.
Patients with a history of herpetic eruptions may experience reactivation
of the herpes.
There is a possible risk of inflammation at the implant site if laser
treatments or a chemical peel are performed after treatment.
Use as supplied. Modification or use of the product outside the Directions
for Use may adversely impact the sterility, safety, homogeneity, or
performance of the product.
For single patient use. Do not reuse a syringe between two treatments
and/or between two patients. Do not resterilize.
Adverse Events
The most commonly reported side effects were firmness, redness,
tenderness, swelling, lumps/bumps, bruising, discoloration, pain and
itching. Most of these events were mild or moderate and resolved within 14
days.
Delayed-onset inflammation near the site of dermal filler injections is
one of the known adverse events associated with dermal fillers. Cases of
delayed-onset inflammation have been reported to occur at the dermal
filler treatment site following viral or bacterial illnesses or
infections, vaccinations, or dental procedures. Typically, the reported
inflammation was responsive to treatment or resolved on its own.
To report an adverse reaction with any RHA® product to Revance,
please visit Safety.Revance.com or call at (877) 373-8669.
RHA® and RHA Redensity® are registered trademarks
of TEOXANE SA, manufactured in Switzerland. The Teoxane RHA® Collection is exclusively distributed by Revance®. All other
trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Available by Prescription only
RHA-00221
REFERENCES 1. RHA® Directions for Use. Nashville, TN: Revance Therapeutics, Inc, 2024. 2. Monheit G, Kaufman-Janette J, Joseph JH, Shamban A, Dover JS, Smith S. Dermatol
Surg. 2020;46(12):1521-1529. 3. Kaufman-Janette J, Taylor SC, Cox SE, Weinkle SH, Smith S, Kinney BM. J Cosmet
Dermatol. 2019;18(5):1244-1253. 4. Sundaram H, Shamban A, Schlessinger J, et al. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48(1):87-93. 5. Data on file. RDRE 2016—US Products, 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: Teoxane, 2016. 6. Faivre J, Gallet M, Tremblais E, Trévidic P, Bourdon F. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47(5):159-167. 7. Data on file. TEO-RHA-1501 Clinical Study Report. Geneva, Switzerland: Teoxane,
2019. 8. Mashburn J, Faivre J, Bourdon F. Evaluation
of the impact of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler manufacturing technologies on HA
chain degradation. Poster presented at AAD VMX, 2021.